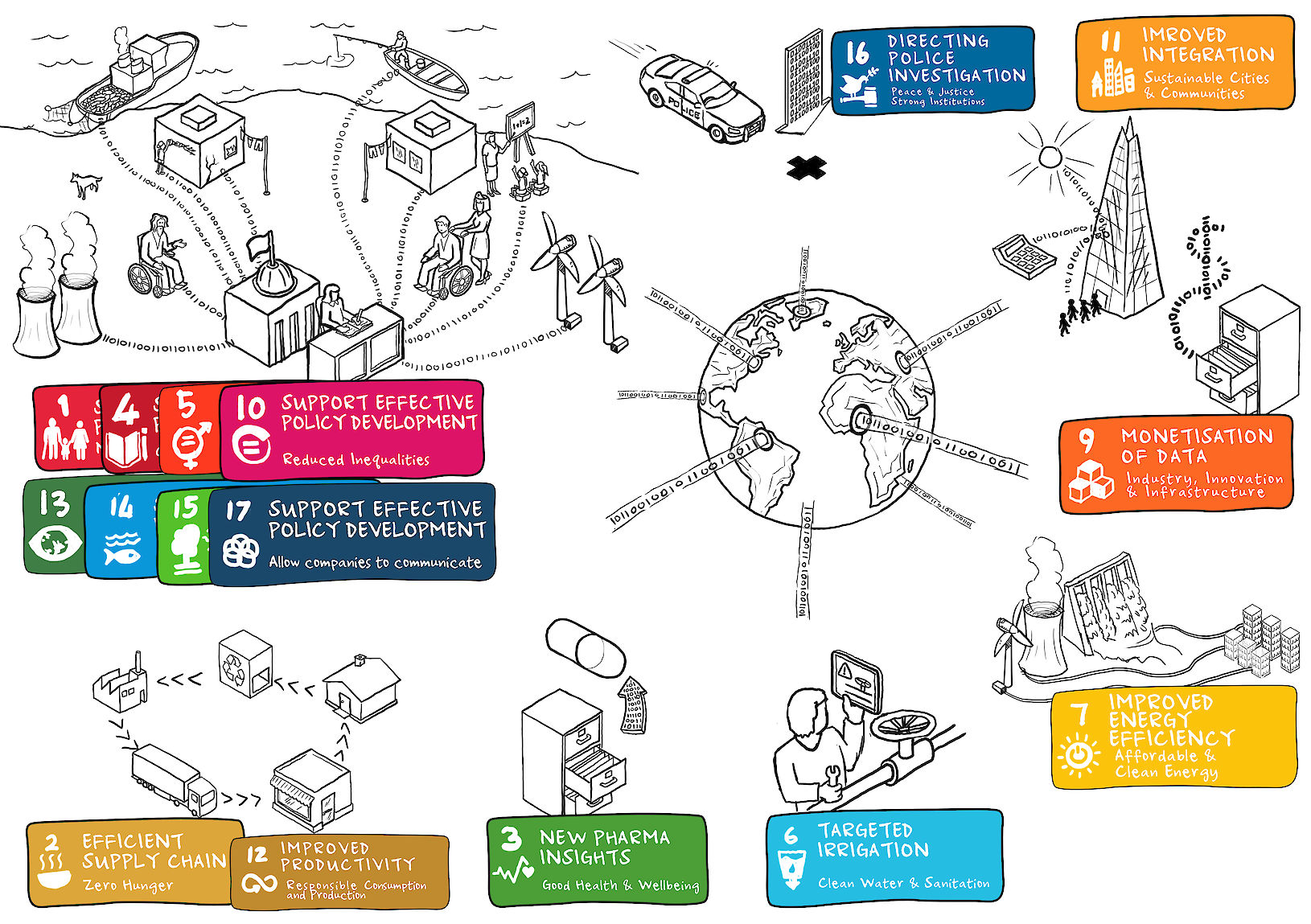
The technology
Big Data relies on computers which can spread the storage and analysis of data across many low cost servers, often hosted in the cloud. There are many ways to analyse this data, ranging from traditional statistical techniques for testing hypotheses to novel approaches identifying objects in images or video data. Often Big Data solutions bring sets of data together in innovative ways to create unexpected answers and insights. These techniques are now more readily available and can be used in ways that make the most of new computing technology.
As well as the computational techniques required to manage this data there have been many advances in analysis and visualisation of the data. These have created new ways of showing information on standard web browsers opening up analysis and understanding to anyone with a personal computer or tablet
The potential
As more aspects of our lives become monitored and connected, it is difficult to imagine an area where Big Data will not make an impact. For example, utility companies are using their measurement and finance data to better predict maintenance routines. Financial institutions can predict risk and monitor fraud more accurately and retailers have used it very successfully to predict customer behaviour. We are all only beginning to fully understand the applications of Big Data techniques and its ability to improve our wellbeing, communities and planet.
The barriers
The major risk with Big Data is the power it gives organisations to monitor multiple aspects of our lives and potentially try to control them. This ranges from the mild irritant of targeted advertising to mass surveillance programmes.